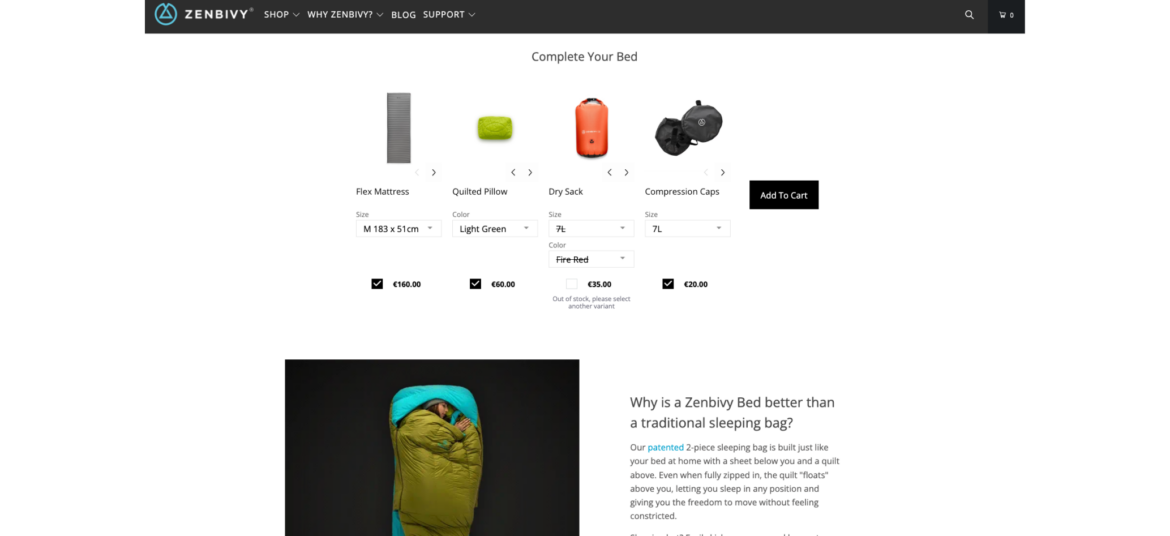
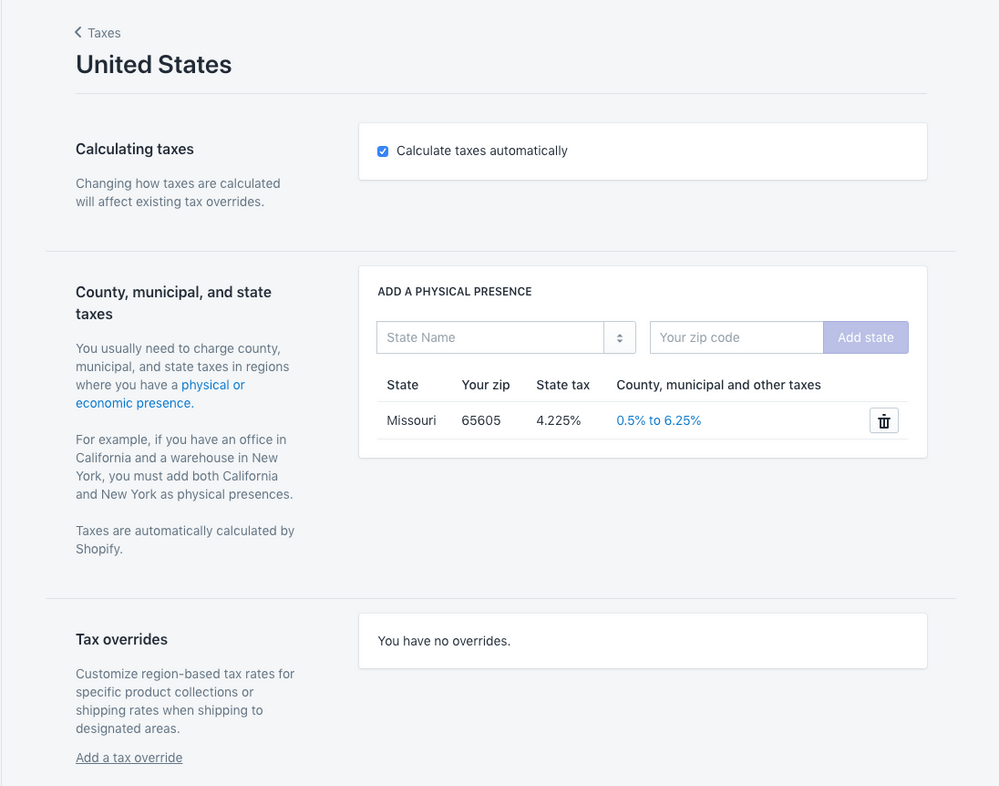
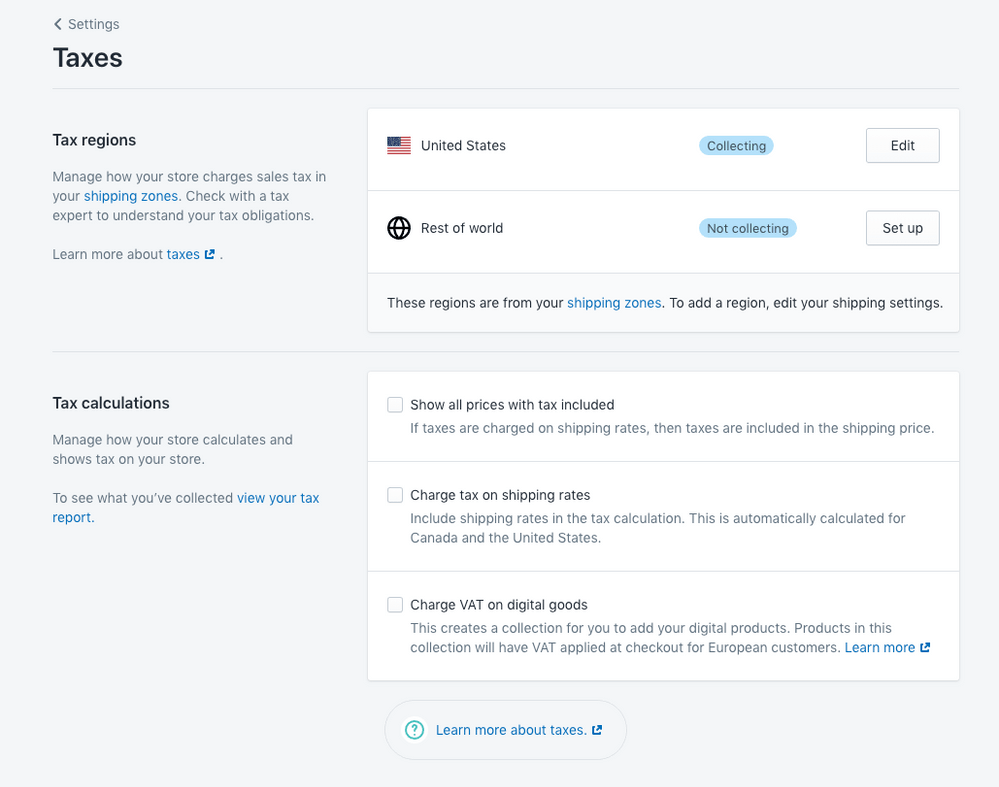
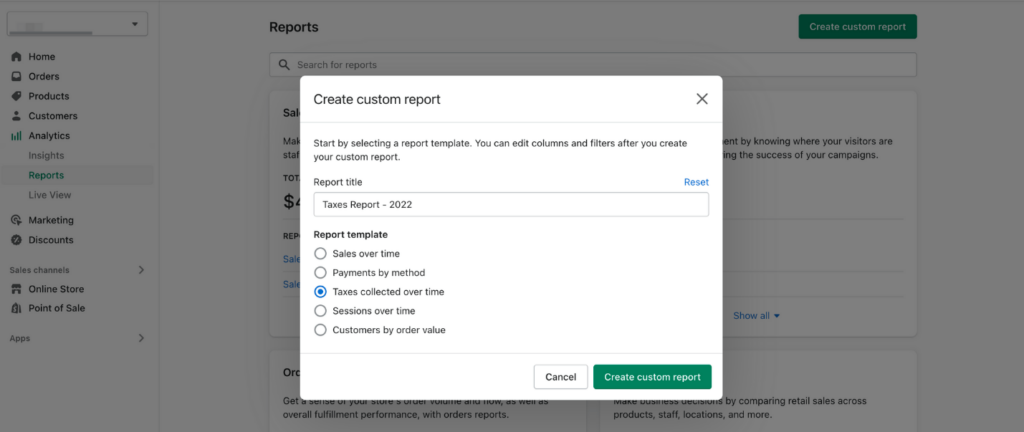
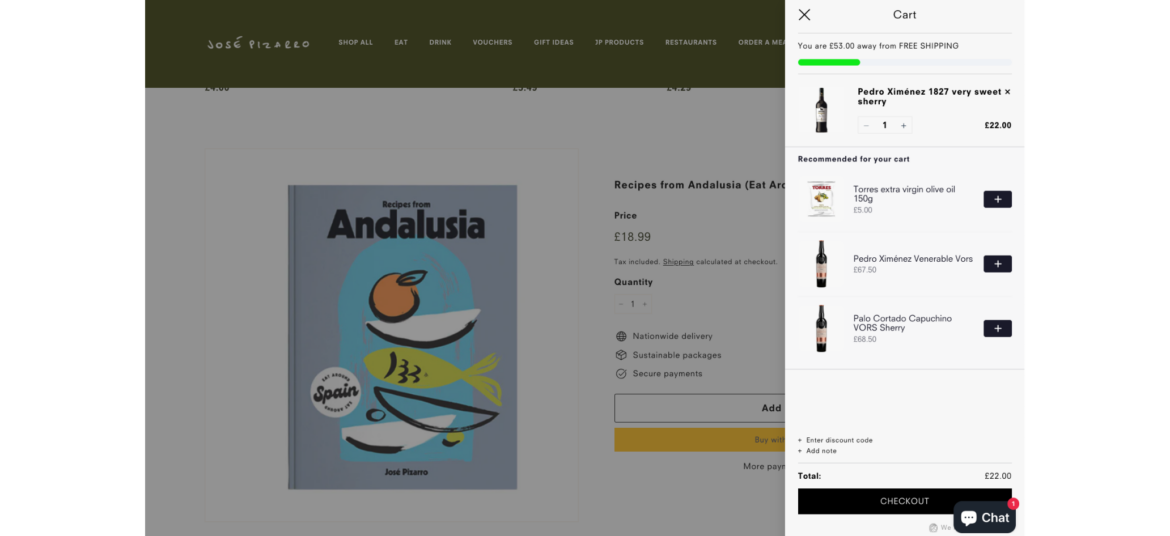
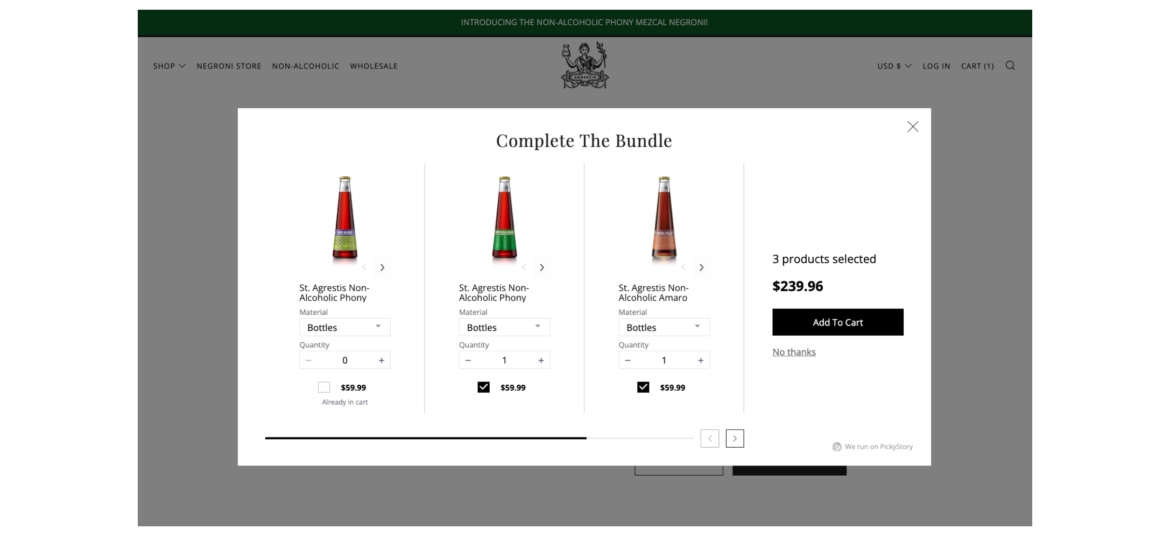
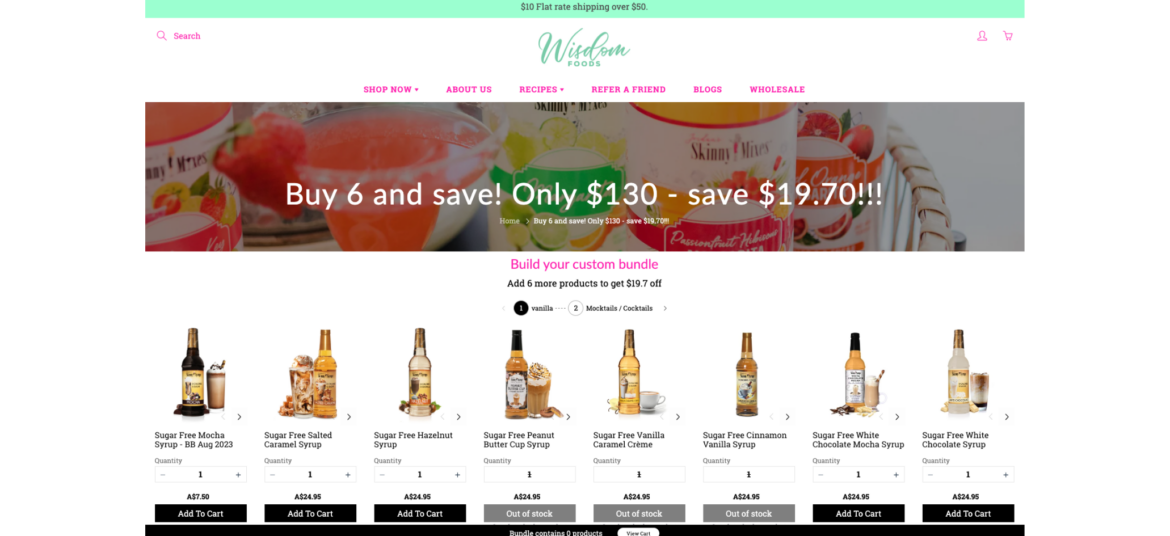
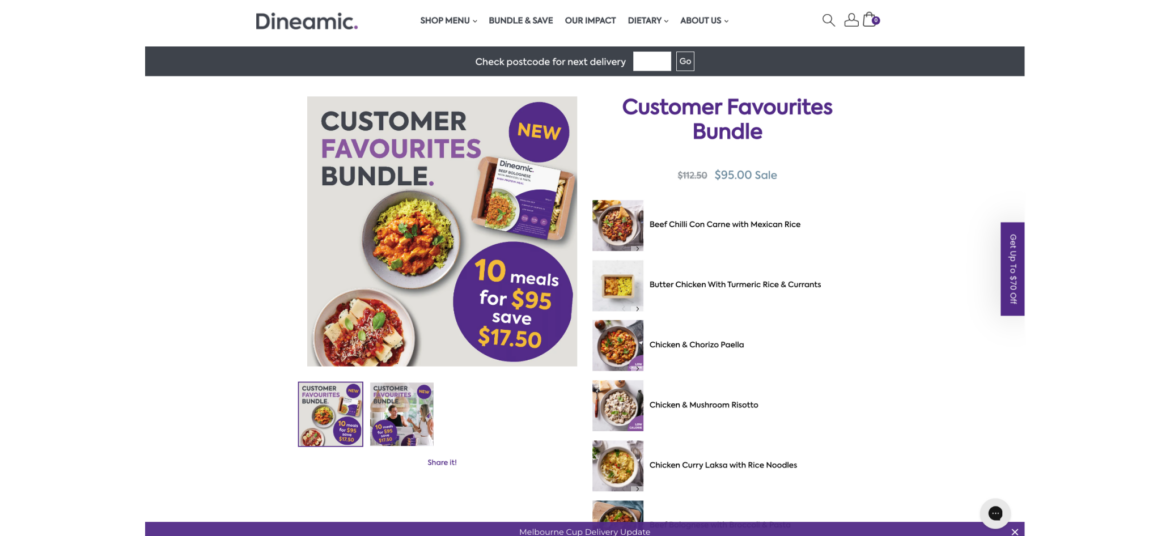
The following list shows the current sales tax by state:
• Alabama: 4.0% to 11.0% (average: 8.91%)
• Alaska: 0.0% to 7.85% (average: 1.76%) – Local jurisdictions impose varying rates.
• Arizona: 5.6% to 11.2% (average: 8.37%)
• Arkansas: 6.5% to 11.5% (average: 9.51%)
• California: 7.25% to 10.5% (average: 8.68%) – Local jurisdictions impose varying rates.
• Colorado: 2.9% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.
• Connecticut: 6.35%
• Delaware: 0.0% – Delaware does not have a statewide sales tax.
• Florida: 6.0% to 8.5% (average: 7.05%)
• Georgia: 4.0% to 8.9% (average: 7.33%)
• Hawaii: 4.0% – Hawaii only has a statewide sales tax; local jurisdictions do not impose additional taxes.
• Idaho: 6.0% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.
• Illinois: 6.25% to 11.0% (average: 8.78%)
• Indiana: 7.0% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.
• Iowa: 6.0% to 7.0% (average: 6.94%)
• Kansas: 6.5% to 10.5% (average: 8.68%)
• Kentucky: 6.0%
• Louisiana: 4.45% to 11.45% (average: 9.52%)
• Maine: 5.5% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.
• Maryland: 6.0%
• Massachusetts: 6.25%
• Michigan: 6.0% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.
• Minnesota: 6.875% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.
• Mississippi: 7.0% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.
• Missouri: 4.225% to 10.35% (average: 8.13%)
• Montana: 0.0% – Montana does not have a statewide sales tax.
• Nebraska: 5.5% to 7.5% (average: 6.84%)
• Nevada: 4.6% to 8.375% (average: 7.78%)
• New Hampshire: 0.0% – New Hampshire does not have a statewide sales tax.
• New Jersey: 6.625%
• New Mexico: 5.125% to 9.0625% (average: 7.82%)
• New York: 4.0% to 8.875% (average: 8.52%) – Local jurisdictions impose varying rates.
• North Carolina: 4.75% to 7.5% (average: 6.97%)
• North Dakota: 5.0% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.
• Ohio: 5.75% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.
• Oklahoma: 4.5% to 11.5% (average: 8.82%)
• Oregon: 0.0% – Oregon does not have a statewide sales tax.
• Pennsylvania: 6.0%
• Rhode Island: 7.0%
• South Carolina: 6.0% to 9.0% (average: 7.78%)
• South Dakota: 4.5% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.
• Tennessee: 7.0% to 9.75% (average: 9.55%)
• Texas: 6.25% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.
• Utah: 4.85% to 8.0% (average: 7.18%)
• Vermont: 6.0%
• Virginia: 4.3% to 7.0% (average: 5.66%)
• Washington: 6.5% to 10.4% (average: 9.23%) – Local jurisdictions impose varying rates.
• West Virginia: 6.0%
• Wisconsin: 5.0% to 5.6% (average: 5.42%)
• Wyoming: 4.0% – Some local jurisdictions may impose additional taxes.